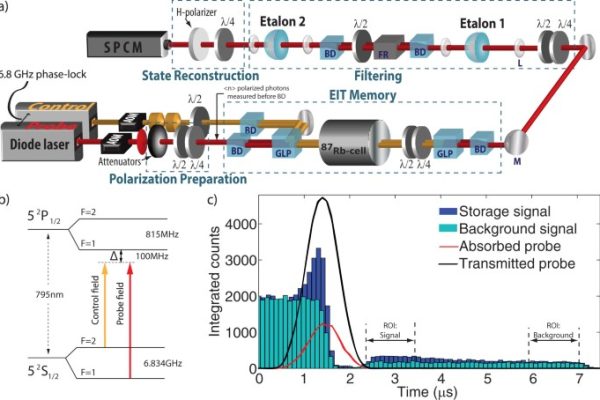
How Biometric Payment Systems Are Shaping the Future of Transactions
As the world becomes increasingly digital, biometric payment systems are revolutionizing how we make purchases—offering speed, security, and convenience in one seamless experience. From fingerprint scans to facial recognition and even palm vein authentication, biometric technology is quickly replacing traditional PINs and cards. Major retailers and fintech companies are investing heavily in biometric infrastructure, citing…